NR vs NMN: What's the Difference?
NR vs NMN? Nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) are both precursors to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that plays important roles in energy production, DNA repair, and other cellular processes.
NR and NMN are often mixed up and confused by most consumers. We will cover the essentials and explain about each of these supplements below.
NAD
NAD is a type of coenzyme found in all living cells. NAD plays important roles in a variety of metabolic reactions, including energy production and DNA repair.
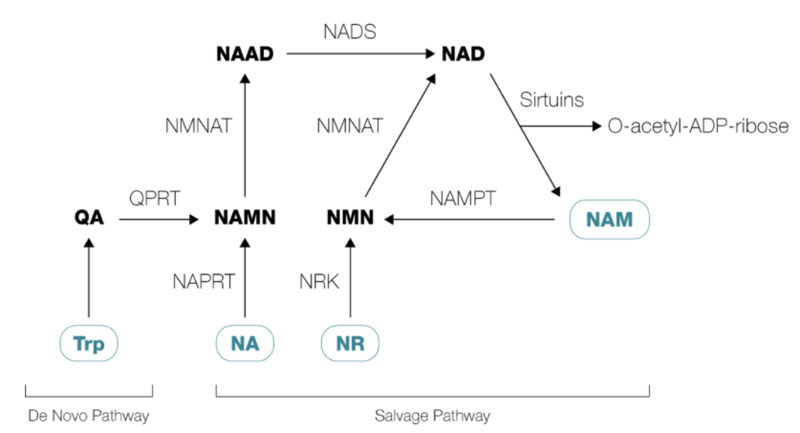
NR, nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), Niacin (NA) and Niacinamide (NAM) are all NAD precursors, meaning all these precursors will be transformed into NAD. That said, each precursor has it's own different pathway that will lead to NAD.
Given that the whole goal of taking NR and NMN supplements is to increase NAD+ levels, why not take NAD+ itself?
The problem is that NAD+ is a large molecule. If you take it orally, it gets broken down in the gut.
The problem is that NAD+ is a large molecule. If you take it orally, it gets broken down in the gut.
NAD+ can however be delivered intravenously, skipping the digestive tract. Some clinics offer NAD+ delivered via an intravenous (IV) injection.
However, intravenous NAD+ causes sudden very high peaks of NAD+ in the blood. Too much NAD+ can perhaps also not be a good thing, for example causing too much reductive stress (R).
However, intravenous NAD+ causes sudden very high peaks of NAD+ in the blood. Too much NAD+ can perhaps also not be a good thing, for example causing too much reductive stress (R).
Furthermore, occasional NAD+ infusions are not ideal. Ideally, NAD+ levels should be increased consistently, such as daily, which can be achieved by taking a daily NMN supplement for a gentler increase in NAD+ levels.
“Therefore, administration of niacin or niacinamide is unlikely to be widely adopted for maintaining health and function with aging,” researchers wrote in Nature Communications.
Within your body, nicotinamide riboside is converted into NAD+, a helper molecule that exists inside each of your cells and supports many aspects of healthy aging.
Nicotinamide riboside supplements — such as niagen — have quickly become popular because they appear to be especially effective at raising NAD+ levels (Source). Nicotinamide riboside is also found in trace amounts in cows’ milk, yeast and beer (Source).
As research grows, it is likely to become clearer that NMN and NR may have differing benefits depending on the part of the body and their use. Where NMN transporters are found, they could make one more preferable over the other. NMN has also been found to improve insulin activity and production which could help to accelerate metabolisms and make the body more glucose tolerant.
NAD is a big molecule relative to vitamin B3. It's got those phosphates on there. It's got a sugar. It's got the vitamin B attached. So you've got all these components that come together to make this very complicated molecule called NAD. And when you give NMN, it contains all three components that the body needs to make NAD. If you give NR or just vitamin B3, which is an even smaller molecule, the body has to find these other components from somewhere else. So where do you get phosphate? Well, body needs it for DNA, needs it for bones. So high doses of something that requires additional phosphate makes me a little concerned, and we have compared NMN and NR head-to-head in mouse studies. We've shown that NMN makes mice run further, old mice can run 50% further because they better blood flow, better energy. NR the same dose did not do that. In fact, it had no effect.
NAD+ for Anti Aging
The levels of NAD in our body determine the speed of aging process. In younger cells and tissues, the levels of NAD are higher. As a result, younger people tend to have better physical activity, cognitive function and potential for cell repair and regeneration. As we grow, the levels of NAD in our body start to decline. This is reflected in the form of slowed cognitive response, loss of memory and reduced agility.
Research suggests it may be possible to reverse mitochondrial decay with dietary supplements that increase cellular levels of a molecule called NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
NAD is a linchpin of energy metabolism, among other roles, and its diminishing level with age has been implicated in mitochondrial deterioration. Supplements containing nicotinamide riboside, or NR, a precursor to NAD that's found in trace amounts in milk, might be able to boost NAD levels. In support of that idea, half a dozen Nobel laureates and other prominent scientists are working with two small companies offering NR supplements.
The NAD story took off toward the end of 2013 with a high-profile paper by Harvard's David Sinclair and colleagues. Sinclair, recall, achieved fame in the mid-2000s for research on yeast and mice that suggested the red wine ingredient resveratrol mimics anti-aging effects of calorie restriction. This time his lab made headlines by reporting that the mitochondria in muscles of elderly mice were restored to a youthful state after just a week of injections with NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide), a molecule that naturally occurs in cells and, like NR, boosts levels of NAD.
Related: NAD Supplements and Cancer
Related: The Crucial Role of NAD+ in Optimal Health
Research suggests it may be possible to reverse mitochondrial decay with dietary supplements that increase cellular levels of a molecule called NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
NAD is a linchpin of energy metabolism, among other roles, and its diminishing level with age has been implicated in mitochondrial deterioration. Supplements containing nicotinamide riboside, or NR, a precursor to NAD that's found in trace amounts in milk, might be able to boost NAD levels. In support of that idea, half a dozen Nobel laureates and other prominent scientists are working with two small companies offering NR supplements.
The NAD story took off toward the end of 2013 with a high-profile paper by Harvard's David Sinclair and colleagues. Sinclair, recall, achieved fame in the mid-2000s for research on yeast and mice that suggested the red wine ingredient resveratrol mimics anti-aging effects of calorie restriction. This time his lab made headlines by reporting that the mitochondria in muscles of elderly mice were restored to a youthful state after just a week of injections with NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide), a molecule that naturally occurs in cells and, like NR, boosts levels of NAD.
NAD+ Helps Restore Age-Related Muscle Deterioration
As reported by Science Daily, scientists recently discovered that Alzheimer's-like protein aggregates underlie the muscle deterioration commonly seen in aging, and that nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is essential for combating this condition.
Their study, published in the journal Cell Reports, showed that protein aggregates (amyloid) could be blocked by boosting the levels of NAD+, a biomolecule that is also essential for maintaining mitochondrial function.
NAD+ boosting molecules such as nicotinamide riboside (NR), nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), nicotinamide (a form of vitamin B3 or niacin) and nicotinic acid (niacin) have all been shown to protect against age-related muscle disease.
Their study, published in the journal Cell Reports, showed that protein aggregates (amyloid) could be blocked by boosting the levels of NAD+, a biomolecule that is also essential for maintaining mitochondrial function.
NR (Nicotinamide Riboside)
There are multiple precursors to NAD+, each with its own physiologic effects. Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a popular one with several notable benefits over other precursors like niacin (NA) and niacinamide (NAM). NA, for instance, may induce uncomfortable flushing, while NAM may inhibit sirtuin at high doses, both undesirable effects.
NIAGEN® is the trade name for Chromadex's proprietary NR ingredient, and protected by patents. Chromadex's finished Niagen product is sold under the brand Tru Niagen.
Because of its unique profile of benefits and low risks, NR has emerged as a popular choice, especially by its discoverer, biochemist Charles Brenner, among the NAD+ precursors. In Scientific Reports, researchers noted:
“Because NR does not cause flushing or inhibit sirtuins and the genes (NRK1 and NRK2) required for the metabolism of NR to NAD+ are upregulated in conditions of metabolic stress, NR has a particularly strong potential as a distinct vitamin B3 to support human wellness during metabolic stress and aging.”
“Therefore, administration of niacin or niacinamide is unlikely to be widely adopted for maintaining health and function with aging,” researchers wrote in Nature Communications.
Within your body, nicotinamide riboside is converted into NAD+, a helper molecule that exists inside each of your cells and supports many aspects of healthy aging.
Nicotinamide riboside supplements — such as niagen — have quickly become popular because they appear to be especially effective at raising NAD+ levels (Source). Nicotinamide riboside is also found in trace amounts in cows’ milk, yeast and beer (Source).
NMN
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a molecule that is a precursor to the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which plays important roles in energy production, DNA repair, and other cellular processes in the body. NMN is a type of nucleotide, which are the building blocks of DNA and RNA.
NMN is found in small amounts in some foods, such as edamame and other types of green vegetables. NMN can also be taken as a dietary supplement, it is used to support the production of NAD+ and is being studied as a potential therapy for age-related diseases and as a way to promote overall wellness and longevity.
NR vs NMN
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) are both precursors to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that plays important roles in energy production, DNA repair, and other cellular processes.
The primary difference is that NR is a form of Vitamin B3 (Niacin), while NMN is a type of nucleotide.
NMN is converted into NAD+ directly by enzymes in the body, while NR needs to go through an additional step in the body in order to be converted into NAD+.
NR is converted into NAD+ in the body and is used to support the production of NAD+ . It is used in therapies for aging, weight loss, and cognitive decline.
NMN is also a precursor to NAD+ and is used to support the production of NAD+ . NMN is a type of nucleotide, which are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, NMN is found in small amounts in some foods, such as edamame.
Both NR and NMN supplements are used to boost NAD+ levels in the body, and are used to support the anti-aging and overall wellness, However, NMN is directly converted into NAD+ by cells, while NR needs to go through an additional step in the body in order to be converted into NAD+.
NR used to be considered superior because no NMN transporter — required to get it into cells — had been detected.
We now know there is such a transporter (published in Nature in 2019: R, R), which gives NMN the advantage as it’s also a more direct NAD+ precursor. However, this is disputed by Chromadex in a 2019 publication.
Chromadex claimed that NMN must first be converted into NR in the blood before it can be used by the cells.
Pitting NR and NMN against each other is, for now, somewhat of a moot point because the two molecules have never been studied side by side in humans. The biggest, and most obvious, difference between NMN and NR is size. NMN is simply larger than NR, meaning it often needs to be broken down to fit into the cell. NR (Nicotinamide Riboside), when compared to other NAD+ precursors (like nicotinic acid or nicotinamide) reigns supreme in efficiency.
But give NMN a new door, one it can fit through, and it’s a whole new game. This is where cellular transporters come into play. Transporters are proteins that are doors on the cell; they allow molecules to enter the cell without needing to chemically transform.
That said, according to David Sinclair in this podcast:
Related:
Supplement manufacturer ChromaDex alleges that testing has revealed that more than half of NMN anti aging supplements being sold on Amazon contained almost none of the bioactive molecule. Source: ChromaDex NMN Report (Oct 2021)
ChromaDex markets TruNiagen, which is based on its branded Niagen ingredient, which is a form of nicotinamide riboside (NR), the form of nicotinamide that actively crosses into the cell to participate in the NAD+ pathway. Boosting this pathway, and thus maintaining cellular function at a lively, youthful level, has become a prominent theme in recent anti aging research.
Recently researchers have argued that a transporter exists for NMN too, which is something that ChromaDex disputes. It claims that NMN must first be converted into NR in the blood before it can be used by the cells.
In the several years since the NMN transporter discovery was asserted, the NAD+ anti aging field has become crowded with NMN based supplements all seeking a piece of the pie created by ChromaDex and its competitor and one time customer Elysium. (The two companies have been locked in various patent infringement and breach of contract suits for several years.)
Last fall, ChromaDex obtained 22 samples of NMN products being sold on Amazon. Of these, 14 claimed to contain 500 mg of NMN. A further two products calimed 300 mg on the label; five claimed 250 mg and one product claimed 125 mg.
Only one of the 500 mg products came close to meeting label claim. It had 456 mg of NMN. All of the other 13 products in the 500 mg group either came in at below reporting limit (BRL, defined as less than 1% of the stated amount) or, in the case of 3 products, no NMN was detected at all.
Almost all of the rest of the products performed better, having at least 88% of the label claim. A lone 250 mg product was identified as BRL.
In summary, ChromaDex said that 64% of the products tested contained less than 1% of the stated amount of the active ingredient, which should give consumers pause, the company said.
"While this is a limited snapshot of the vast NMN finished product landscape, it does provide a glimpse into the high variability of product quality that is available... According to this study, the majority of the products one might purchase online contain such a small amount of NMN that there would be no clinical benefits achieved from the dose. Another concern with these adulterated products is that the actual contents are not known and could pose a risk to the user," the company said in a statement.
Editor's Note: In February 2022, another third-party investigation uncovered tens of thousands of fake supplements sold on Amazon. Many of these included NMN.
Can you take NR and NMN together?
There have been no studies on taking NMN & NR together, and it would be best to test both separately and find which one you respond better to. You may be wasting your time (and money) taking both NMN & NR together as studies show that the majority of the time, NR is turned into NMN which is then turned into NAD+.Stability and storage of NMN and NR
A stability analysis demonstrates NR is stable (does not undergo degradation) for up to six hours at room temperature and seven days at two to eight degrees Celsius. Regarding stability of NMN and NR, David Sinclair, PhD, A.O. of Harvard University says, “Make sure your NR and NMN is kept in the cold. If it’s just on the shelf and it’s not in a stabilized form, then it will degrade to nicotinamide, which is something you don’t want to take high doses of because we’ve shown in my lab many years ago that nicotinamide will inhibit the sirtuins, and PARP as well, and interfere with DNA repair.”How can I raise my NAD levels naturally?
If you want to remain youthful and enjoy a long and healthy life, then there are ways in which you can naturally enhance the levels of NAD in your body. Continue reading to find out how:
1. Fasting
Fasting is practiced in many religions throughout the world. In addition to its spiritual benefits, it turns out that fasting is also beneficial for our health. Fasting, or reducing your calorie intake is an excellent method for indirectly boosting the body’s NAD levels. Fasting has been shown to increase the levels of NAD+ and surtuins; the proteins which have been found to slow the aging process.
While fasting is effective in increasing NAD+ levels, drastic reduction in calorie intake or fasting can have a counterproductive effect. There is also some speculation that intermittent fasting or adopting a low carb-ketogenic diet may also provide similar positive results.
2. Nicotinamide Riboside and other NAD Boosting Dietary Supplements
Nicotinamide Riboside has recently been discovered in Vitamin B3. No one really paid attention to this molecule until research showed that our bodies can use NR to metabolise NAD+! After this discovery, several NR supplements became available in the markets. Various studies have shown that NR supplements are beneficial in boosting the levels of NAD+ in the body.
3. Exercise
Exercise is one of the easiest and most cost-effective methods for boosting NAD+ levels. When we exercise, our bodies need energy, which comes from NAD+. Basically, exercise forces our body muscles to produce more mitochondria, which are the powerhouses of cells. The increased production of mitochondria results in a natural boost in NAD+ levels in the body.
4. Too Much Sunlight May not be Good!
Research has shown that too much direct sunlight exposure can deplete the body of NAD+ levels. This is because our body uses NAD+ to repair cells which get damaged as a result of direct UV ray exposure from the sunlight. In case you feel that excessive sunlight exposure is inevitable for you, then you should wear sunblock, sunscreen or sunglasses.
5. Foods which Boost NAD Levels
There are certain foods which can boost NAD levels in the body. Some of them include:
- Dairy Milk – research has indicated that cow’s milk is a good source of Nicotinamide Riboside (NR). A litre of fresh cow’s milk contains about 3.9µmol of NAD+.
- Fish – some varieties of fish like tuna, salmons and sardines are rich sources of NAD+ for the body.
- Mushrooms – many people like mushrooms and them as a regular food item in their regular diet. But did you know that mushrooms, especially the crimini mushrooms, also help in naturally boosting NAD levels? Yes, that’s true. So, enjoy eating the mushrooms and continue to look and younger and more youthful!
- Yeast – yeast is an ingredient which is used for making bread and other bakery products. Yeast contains Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), which is a precursor of NAD. Here’s another reason for you to enjoy your favorite pastries or buns whenever you visit the bakery! Enjoy your favorite food while boosting NAD levels at the same time.
- Green Vegetables – green vegetables contain all sorts of nutrients in them which are beneficial in a variety of ways. Recently, it has come to light that green vegetables are also a good source of NAD for the body. Some of these vegetables include peas and asparagus.
- Whole Grains – as discussed earlier, Vitamin B3 also contains Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), the precursor for NAD. However, when vegetables, food items or grains are cooked or processed, they lose their nutrition as well as the vitamin source. Therefore, it is recommended that you should also eat raw vegetables and take whole grains instead of processed foods.
- Cut Down on Alcoholic Beverages – NAD is responsible for maintaining the overall metabolic processes of the body. Alcohol tends to interfere with these processes and reduce the efficacy of NAD. Therefore, you should avoid excessive intake of alcoholic drinks since they are also not good for your health.
Key Takeaways
It should be stressed that increasing NAD alone may not be enough to decelerate your aging process. High energy carrying molecules like ATP, antioxidants like glutathione and hormones like the stress hormone, cortisol also play a significant role in the aging process.
If your objective is to live a longer, healthier life, a study conducted by Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health lays out five practices, none of which needs to involve a fad.
The five low-risk factors are the following:
1. Avoid smoking. Low risk is defined as low exposure to smoking.
2. Maintain a healthy weight. Low risk is defined as a Body Mass Index in the range of 18.5 to 24.9. BMI is a ratio of weight to height that, though imperfect, offers a quick and easy assessment of weight status.
3. Exercise regularly. Low risk is defined as moderate- or vigorous-intensity exercise for 30 or more minutes a day.
4. Consume moderate amounts of alcohol. Low risk is defined as one-half to one drink per day for women and one-half to two drinks per day for men.
1. Avoid smoking. Low risk is defined as low exposure to smoking.
2. Maintain a healthy weight. Low risk is defined as a Body Mass Index in the range of 18.5 to 24.9. BMI is a ratio of weight to height that, though imperfect, offers a quick and easy assessment of weight status.
3. Exercise regularly. Low risk is defined as moderate- or vigorous-intensity exercise for 30 or more minutes a day.
4. Consume moderate amounts of alcohol. Low risk is defined as one-half to one drink per day for women and one-half to two drinks per day for men.
Editor's view: We are not big fans of consuming alcohol.
5. Maintain an overall healthy diet. Low risk is defined as a diet with high intakes of vegetables, fruit, nuts, whole grains and long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, and low intakes of red and processed meats, sugar-sweetened beverages, trans fat and sodium.
5. Maintain an overall healthy diet. Low risk is defined as a diet with high intakes of vegetables, fruit, nuts, whole grains and long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, and low intakes of red and processed meats, sugar-sweetened beverages, trans fat and sodium.


Comments
Post a Comment